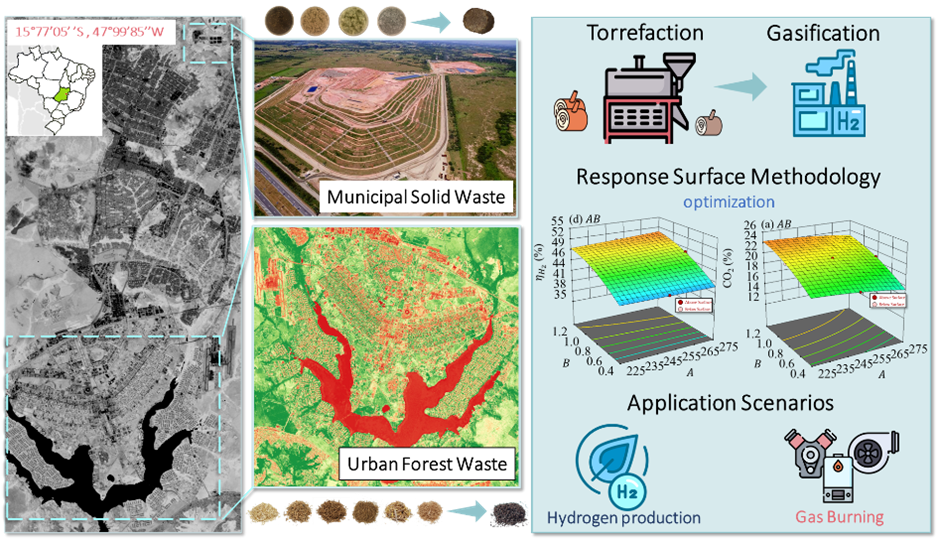
This study aims to simulate the steam-enhanced co-gasification of hybrid blends (HB) composed of municipal solid waste (MSW) and urban forest waste (UFW), with torrefaction as pretreatment. Experimental (torrefaction), numerical (gasification thermodynamic equilibrium model), and optimization (response surface methodology) techniques evaluated the gasification process to produce (i) hydrogen-rich gas or (ii) enhanced calorific value gas. The torrefaction (225–275 °C), steam-to-biomass (0.4–1.2 S/B) ratio, and HB proportion (0–50% of MSW) influences were investigated to assess H2%, exergy efficiency of H2-production (effH2), lower heating value (LHV), cold gas efficiency (CGE), and CO2%. The hybrid methodology defined the optimal conditions for 600 °C gasification as (i) 0.9 S/B and an HB comprising 31% MSW and 69% torrefied UFW at 275 °C, presenting an effH2 of 49%; and (ii) 0.4 S/B and an HB containing 23% MSW and 77% torrefied UFW at 275 °C, showing an LHV of 6126 kJ.Nm−3